
What Is Net Income Growth and Why Does It Matter?
An increase in net income means an increase in profit recognized by the entity during a specific period. This indicates how efficiently and effectively a business can convert amounts into real profits from revenues after deductions of expenses, taxes, and costs. The growth in net income is a very important measure to assess the health and sustainability of any corporation.
It reflects the facts for an investor that a continuously increasing net income indicates:
- Good management
- Scalable operations
- Financial viability
All of which contribute to rising stock valuations.
How to Measure Net Income Growth
There are several methods to measure net income growth, each suited to different timeframes and levels of detail:
Period-Over-Period (PoP) Growth

Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR)
Useful for multi-year analysis, CAGR smooths out fluctuations:
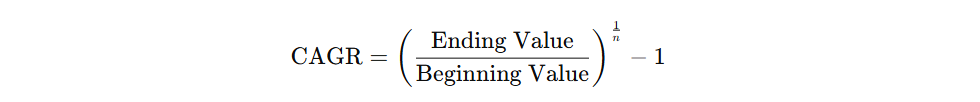
Where n is the number of years.
Comparing Year-over-Year (YoY) or Quarter-over-Quarter (QoQ) figures helps spot trends and detect anomalies in profitability.
Net Income Growth Formula and Examples
Example:
| Year | Net Income ($M) |
| 2022 | 500 |
| 2023 | 600 |
Calculation (PoP Method):
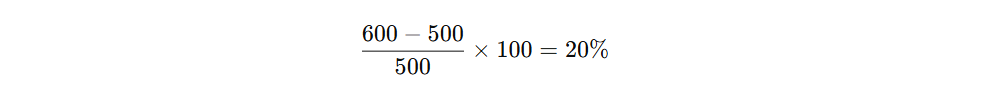
The company achieved 20% net income growth YoY.
This example illustrates how modest income gains can significantly boost investor confidence—especially when paired with stable revenue and margin improvements.
Tools for Automatic Net Income Growth Calculation
Investors can streamline analysis using tools like:
- Excel or Google Sheets (with custom formulas)
- Financial platforms like Morningstar, YCharts, or TradingView
- Brokerage dashboards offering growth metrics in summary tables
Automated tools minimize calculation errors and help visualize trends across multiple reporting periods.
Key Drivers of Net Income Growth
Net income growth depends on various internal and external factors:
Internal Drivers:
- Sales and revenue expansion
- Operational efficiency and cost control
- Innovation and pricing power
External Drivers:
- Interest rates and tax policy
- Industry dynamics and market share shifts
- Currency fluctuations for global firms
Monitoring these elements helps investors forecast future income trends with greater accuracy.
Common Pitfalls in Measuring Net Income Growth
Some common issues can distort net income trends:
- One-time gains or losses from asset sales or lawsuits
- Accounting adjustments that do not reflect operational performance
- Seasonality in sectors like retail or agriculture
- Comparisons across economic cycles (recession vs. expansion)
Context matters—growth should be evaluated alongside other metrics like EBITDA, margins, and revenue trends.
Why Net Income Growth Influences Stock Valuation
Stock prices are fundamentally tied to earnings. When net income grows consistently:
- Price-to-Earnings (P/E) ratios become more favorable
- Analysts revise price targets upward
- Institutional buying interest increases
Impact Table:
| Factor | Influence on Stock Price |
| Strong Net Income Growth | Positive market sentiment |
| Stable Margins | Confidence in sustainability |
| Increasing EPS | Attractiveness to long-term funds |
Growth in earnings signals value creation, which the market typically rewards with higher valuations.
Strategic Use of Net Income Growth in Investing
Short-Term Approach:
- Traders may use earnings momentum to time entries around quarterly reports.
Long-Term Strategy:
- Fundamental investors assess net income growth trends to identify sustainable compounders.
Checklist Before Investing:
- Is the growth organic or acquisition-driven?
- Are margins improving alongside earnings?
- Is growth sustainable across economic cycles?
Combining earnings growth with qualitative insights can improve risk-adjusted returns.
Conclusion: Understanding Net Income Growth as a Valuation Catalyst
Net income growth is more than just a profitability figure—it’s a barometer of corporate efficiency, market strength, and financial discipline.
For investors, it offers a direct link to valuation potential, especially when supported by solid fundamentals and transparent financial reporting.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a good net income growth rate?
A rate of 10–15% annually is considered solid for established companies, while high-growth firms may aim for 20%+.
How does net income growth differ from revenue growth?
Revenue reflects sales; net income accounts for costs, taxes, and depreciation—offering a clearer view of actual profitability.
Can a company have revenue growth but negative net income growth?
Yes. Rising costs, debt interest, or poor expense management can erode net income despite higher sales.
Is net income growth the best metric for stock selection?
It’s one of the most important, but should be used alongside other metrics like free cash flow, ROE, and profit margins.
